
Did you know that Disney was the first to produce a feature-length animated film? In 1937, The Walt Disney World Company released Snow White and became one of the largest media and entertainment companies. The company took a twisted road to success, and there’s a lot a student can learn from a Disney case study.
📠 Disney Facts No One Told You Before
- The Walt Disney Company was founded in 1923 by brothers Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney.
- Reaching the $1 billion box office mark is considered a significant achievement in the film industry. The first of Disney’s films to reach this landmark was the 2006 film “Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man’s Chest.”
- Although Disney World in Orlando is considered the most popular Disney theme park, it wasn’t the first. The first resort and theme park created by Walt Disney is Disneyland in California.
- One of Disney’s most significant acquisitions was when it acquired Marvel Entertainment for $4.24 billion.
- Overall, Disney is a highly profitable company. However, the most profitable segment is Media Networks, which encompasses the Disney Channels and the ABC Family.
💼 Disney Case Study – Best Ideas
Disney company includes various business units that work together to achieve high financial performance. Here are some ideas for your Disney case study!
- The corporate history.
- Company units and divisions.
- Disney’s content groups.
- Mission and values.
- Board of directors and executives.
- Marketing strategy.
- Digital marketing solutions.
- HR practices and training at Disney.
- Labor standards.
- Criticism of the company.
- Corporate social responsibility.
- Disney’s environmental goals.
- Disneyland parks and resorts.
- Main competitors.
- Company’s strategic planning.
- Leadership principles in Disney.
- Crisis management strategy.
📋 Disney Corporate-Level Strategy
- The restructuring of Disney’s Media Networks
Media Networks were the critical business element of The Walt Disney Company that oversaw the company’s cable channels, television production, and distribution studios. However, in 2020 the segment was restructured into Disney Media and Disney General Entertainment Content. - Disney’s parks, experience, and consumer products
This new business segment connects Disney’s consumer products with Walt Disney parks and resorts. Disney’s global consumer products include toys, apparel, home goods, and apps. By uniting Disney’s consumer products and Disney parks, the company provides consumers with a more excellent experience. - Direct-to-consumer Disney vs. International Disney
These two segments make Disney a global, multiplatform organization. To make Disney accessible to every consumer all over the globe, the company introduced Disney+, a streaming service. The service primarily distributes films produced by The Walt Disney Studios with dedicated content hubs for the brands like Pixar, Marvel, and Star Wars.
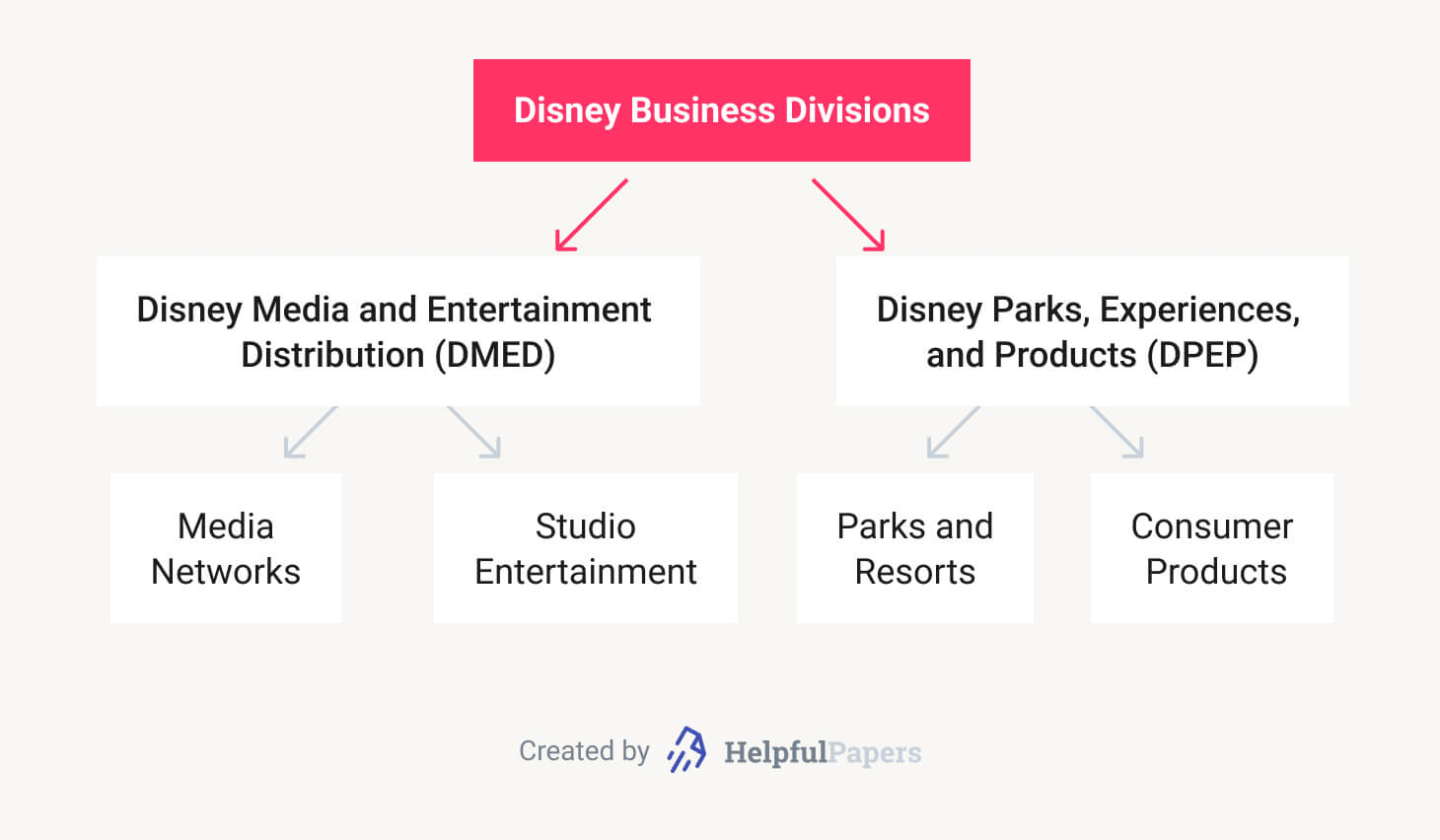
🤝 Disney Organizational Structure
- The Walt Disney Company’s organizational structure type
The foundation of Disney’s company is the cooperative multidivisional structure. The business-type segments in Disney’s organizational structure are:- Media Networks
- Parks and Resorts
- Studio Entertainment
- Consumer Products
- Disney’s functional groups
Disney’s functional groups are responsible for corporate centralization throughout the multinational business. For example, characters from new movies are used in the company’s Disneyland amusement parks and merchandise. - Disney’s geographical divisions
The company considers the culture of its consumers in a particular country and adapts to specific market conditions. Disney’s geographical divisions include:- The United States
- Canada
- Europe
- The Asia Pacific
- Latin America
- The Walt Disney Company’s corporate structure: advantages & disadvantages
Disney’s organizational structure has centralized managerial control, necessary for cooperation among the company’s business segments. However, there are some branding-associated limits in product development that Disney experiences.
Disney’s presence in Canada is an example of how the company adapts its organizational structure to different markets while preserving its global brand identity. If you are assigned to write a case study on this or similar topic, it’s important to highlight how corporations balance global centralization with local responsiveness. Experts from Custom-Writing.com can help you present all the insights in a clear and academically sound way. On this platform, you will find specialists who, apart for awareness of local Canadian context, have expertise in academic writing and research.
🤑 Disney Case Study Strategic Management
- Disney’s mission and vision
According to the company’s website, its mission is to be one of the world’s leading entertainment producers, using its portfolio of brands to provide the best content, services, and products. The company’s vision is to lead the industry to diversification by emphasizing family values. - Disney’s current and future strategic environment
Disney Company operates in the diversified entertainment industry, with numerous competitors. The list of the main Disney rivals includes Universal, Sony, and Time Warner. Disney plans to pay closer attention to theatrical distribution to maintain its leadership after Covid-19 is over. - Disney’s prospects and market entry
Disney focuses on its international operations, trying to expand into new markets worldwide. An example is the company’s plan to open a direct-sale store in China.
🛍️ Disney Digital Marketing Case Study
- Disney’s engaging marketing campaigns
Disney uses storytelling technique for the majority of their e-marketing campaigns. For example, the #DreamBigPrincess initiative was developed to encourage kids worldwide to dream big and follow their dreams. The company challenged photographers to take powerful photos of real-life female role models, including influencers and women in sports. - Disney organizing anniversary celebrations
In 2020, Disney announced a virtual family festival called “Pixar Fest” to celebrate the 25th anniversary of Pixar’s Toy Story. The celebration started with an epic collection of Pixar movies on the Disney+ channel, special masterclasses, the releases of new products, and fun quizzes for movie lovers. The event brought considerable attention to Disney’s social media, including Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. - Disney’s marketing strategy: customer loyalty
Disney reshares old content long after its first release as a part of its digital marketing strategy. To maintain customer loyalty, Disney brings up old classics such as Aladdin, The Lion King, and The Jungle Book to make people feel nostalgic. Another example is how hard Disney’s moviemakers worked on the new version of the Lion King to make the remake with the same characters and story.

💪 Disney Case Study Crisis Management
- Disney and Scarlett Johansson lawsuit
A Disney movie Black Widow debuted simultaneously in cinemas and via the Disney+ streaming service. Scarlet Johansson decided that the company sacrificed the film’s cinema potential to grow its streaming service and filed the lawsuit. Luckily, the legal dispute was soon settled, and the agreement’s details were not disclosed. - The crisis during Disney’s celebration in 2016
Disney’s Orlando theme park had a reputation for a secure and exciting environment. However, the death of 2-year-old Lane Graves almost destroyed the Disney empire. After the tragedy, Disney’s team immediately installed barriers to all ponds on the resort property. - Disney responding to COVID-19
The COVID-19 pandemic has dramatically impacted Disney. Over 100,000 staff at Disney theme parks were put on indefinite unpaid leave in 2020. The company experienced dramatic financial losses but managed to support the employees with the help of streaming services.
🏰 Euro Disney Case Study
- The history of Euro Disney
The park named Euro Disney opened in Paris in 1992. People had huge expectations, but financial problems and other issues would impact Disneyland Paris for years. Many companies, such as Coca-Cola, jumped at the opportunity to share Euro Disney’s success. However, those companies didn’t know that having a part in the new expansion of Disney would also cause them to be included in multiple problems. - The disaster of Euro Disney
From the beginning, Euro Disney was perceived as an assault on French culture. The minister of culture even announced boycotting the opening of this “symbol of American cliches and consumer society.” However, one of the crucial problems was that Europeans didn’t stay at the park as long as Disney expected. The theme park was a place for day excursions for most Europeans, not an extended vacation. - The three lessons to learn from the Euro Disney case
The first lesson is that multinational companies should target the foreign market accurately, considering regional cultural peculiarities. Moreover, international businesses should be good at collaborating with the authorities of different countries. Finally, it is necessary to adapt to the host’s cultural environment and values and carry out the business strategy.
🎞️ Disney and Pixar Merger Case Study
- Reasons for Disney and Pixar merger
By acquiring Pixar, Disney was getting help with content generation and maximizing profit. For Pixar, this deal was beneficial in gaining monetary support from Disney. It also gave Pixar a better position in the market against competitors like DreamWorks, Universal, etc. - The benefits for Disney and Pixar
The deal happened at the perfect timing for Disney, as its animation films were failing without Pixar’s necessary technologies. For Pixar, that was an opportunity to focus on its core strengths of producing computer animation instead of investing in the production line for making merchandise. - The results of the Disney and Pixar merger
In the interview, Disney’s ex-CEO Bob Iger said he is proud of this acquisition. However, when Disney first announced the acquisition, some analysts felt they had paid too much for the animation studio. Disney and Pixar created “Frozen,” “Moana,” and other animated movies that won Academy Awards by 2021.
🎁 More Disney Case Study Ideas
- The organizational structure of Walt Disney Company.
- Management principles at Disney.
- Leadership style at Disney company.
- Disney company’s international marketing.
- Employee motivation strategy at Disney.
- Disney’s financial performance over the years.
- Disney company’s strategic decision-making.
- The Walt Disney Company’s brand identity.
- The Walt Disney Company’s strategic management.
- Key partnerships with The Walt Disney Company.
- Use of social media for marketing at Disney.
- Walt Disney Parks and Resorts Inc. in China.
- Walt Disney Company’s conflicts management.
- Walt Disney Parks and Resorts: supply and value chain.
- The Walt Disney Company’s marketing strategies.
- Euro Disney: strategic human resource practices.
- Disney company’s SWOT analysis.
- The biggest strategic challenges of The Walt Disney Company.
- Disney World and consumer behavior.
- The role of technology and innovation at Disney.
- Disney’s key market competitors.
- Employment and internships in Disney company.
- The evolution of Disney movies over the years.
- Analysis of plagiarism in some works of The Walt Disney Company.
- The influence of Disney on children’s culture.
- Disney company’s collaborators and competitors.
- Disney company’s international strategy.
- Consumer perception of The Walt Disney Company.
- Principles of team management at Disney.
- Performance evaluation of Disney company.